
You need not reboot your system for the change to take effect, just make the Linux system aware about the modification you have made to the /etc/fstab file. dev/sda7 /chroot ext2 defaults,noatime 1 2 In our example below, we will set the noatime option to our /chroot file system.Įdit the fstab file vi /etc/fstab and add in the line that refer to /chrootfile system the noatime option after the

Note that the write time information to a file will continue to be updatedĪnytime the file is written to. Since writes can be somewhat expensive, this can result in measurable performance gains. The importance of the noatime setting is that it eliminates the need by the system to make writes to the file system for files which are simplyīeing read.
FSTAB DEFAULTS UPDATE
IfĪ file system has been mounted with this option, reading accesses to the file system will no longer result in an update to the atime information associated with the file like Linux has a special mount option for file systems called noatime that can be added to each line that addresses one file system in the /etc/fstab file.
FSTAB DEFAULTS MANUAL
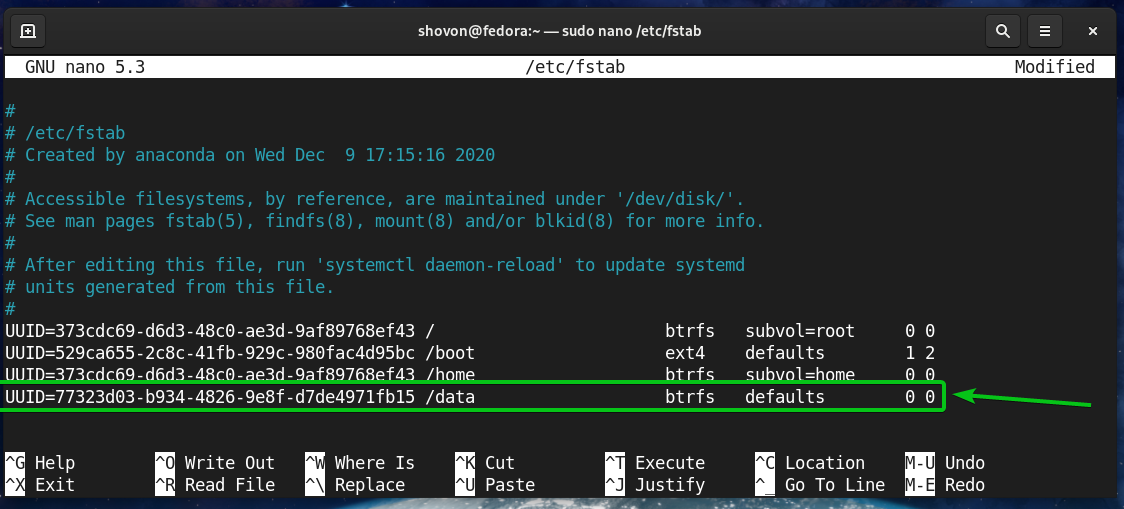
Re: /etc/fstab defaults means also acl Post by TrevorH » Thu 5:17 pm It depends on the filesystem but acl has been default on ext3/4 filesystems for some time. TrevorH Forum Moderator Posts: 32156 Joined: Thu 10:40 am Location: Brighton, UK. The mtab file is the list of currently mounted file systems. If only there was a neat way to get the settings you need, in the order you need to enter them into the fstab file. Default file system mount attributes can be overridden in /etc/fstab. Some file systems such as XFS enable ACLs by default. Modern Red Hat based systems set ACL support as default on the root file system but not on user-created ext3 filesystems. You can add or remove further options if some fine-tuning is required. The normal default for ext3 file systems is equivalent to rw,suid,dev,exec,auto,nouser,async. That might be exactly what you want for e.g. /etc/fstab << here defaults to put a fs means also acl Top. The defaults option is a good opening gambit. It will halt the boot process if such filesystems cannot be checked, except when the mount option nofail is given.Ī possible disadvantage of nobootwait is that, if the disk is actually present, it will do the filecheck in the background and continue booting. Non-critical drives typically have this field set to 2.

This file uses the following format template. Both real and virtual filesystems are listed (like the swap space).

It will halt the boot process if such entries cannot be mounted, except when the mount option nobootwait is given. On many Unix systems, the /etc/fstab file (commonly called the 'Filesystem Table') lists filesystems that will be mounted on boot-up.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
